Embark on an enlightening journey into the realm of dynamics with the Newton’s Second Law of Motion Problems Worksheet. This comprehensive resource empowers you to delve into the intricacies of Newton’s second law, equipping you with the tools to conquer a multitude of real-world challenges.
As we delve deeper into this worksheet, you will gain a profound understanding of Newton’s second law, its mathematical formulation, and its indispensable role in solving problems involving force, mass, and acceleration. Through a series of meticulously crafted practice problems, you will hone your analytical skills and develop a mastery of this fundamental principle of classical mechanics.
Newton’s Second Law of Motion: Definition and Formula
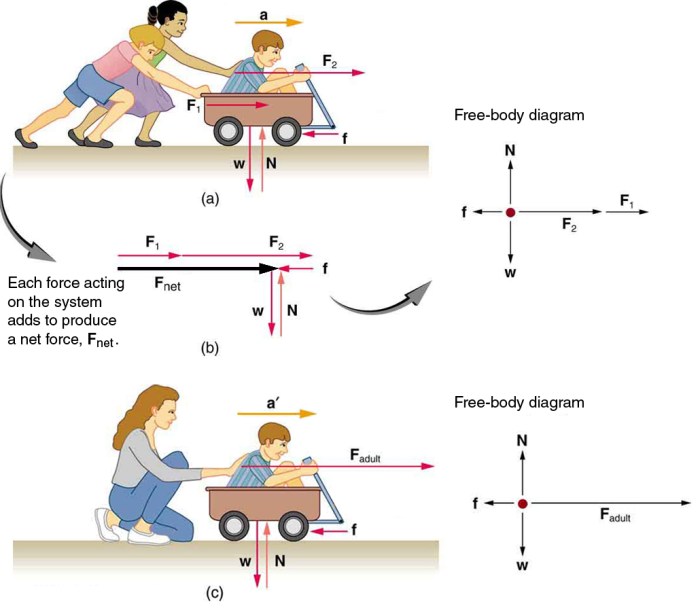
Newton’s second law of motion, also known as the law of acceleration, describes the relationship between an object’s mass, its acceleration, and the forces acting upon it. The law states that the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting on the object, and inversely proportional to the object’s mass.
The mathematical formula for Newton’s second law of motion is:
F = ma
where:
- F is the net force acting on the object (in newtons)
- m is the mass of the object (in kilograms)
- a is the acceleration of the object (in meters per second squared)
Solving Problems Using Newton’s Second Law: Newton’s Second Law Of Motion Problems Worksheet

To solve problems using Newton’s second law, follow these steps:
- Identify the forces acting on the object.
- Draw a free-body diagram of the object, showing all the forces acting on it.
- Calculate the net force acting on the object.
- Use Newton’s second law (F = ma) to calculate the acceleration of the object.
Here is a table that shows how to fill in the table to solve problems using Newton’s second law:
| Mass (kg) | Acceleration (m/s^2) | Force (N) |
|---|---|---|
| m | a | F |
Applications of Newton’s Second Law
Newton’s second law of motion has a wide range of applications in real-world scenarios, including:
- Engineering: Newton’s second law is used to design and analyze structures, machines, and vehicles.
- Physics: Newton’s second law is used to study the motion of objects, from the smallest particles to the largest galaxies.
- Sports: Newton’s second law is used to analyze the performance of athletes and to design training programs.
Limitations and Extensions of Newton’s Second Law, Newton’s second law of motion problems worksheet
Newton’s second law of motion has some limitations. It is only valid for objects moving at speeds much less than the speed of light. For objects moving at relativistic speeds, Einstein’s theory of relativity must be used.
Newton’s second law can also be extended to include the effects of friction and other non-conservative forces. These extensions are known as the laws of motion with friction.
FAQ Resource
What is Newton’s second law of motion?
Newton’s second law of motion states that the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting on the object, and inversely proportional to its mass.
How do I use Newton’s second law to solve problems?
To solve problems using Newton’s second law, you need to identify the forces acting on the object, determine the net force, and then use the equation F = ma to calculate the acceleration.
What are some applications of Newton’s second law?
Newton’s second law has applications in a wide range of fields, including engineering, physics, and sports. It is used to design bridges, rockets, and airplanes, to calculate the forces acting on athletes, and to understand the motion of celestial bodies.