Atoms Have Subatomic Particles Concept Map: Embark on an enthralling journey into the fundamental building blocks of matter. This concept map meticulously unravels the intricate structure of atoms, revealing the enigmatic world of protons, neutrons, and electrons.
As we delve deeper into the properties and interactions of these subatomic particles, we gain invaluable insights into the very essence of matter. Prepare to witness the electromagnetic force orchestrating the dance between protons and electrons, while the strong nuclear force forges an unbreakable bond between protons and neutrons within the atomic nucleus.
Definition of Atoms and Subatomic Particles: Atoms Have Subatomic Particles Concept Map
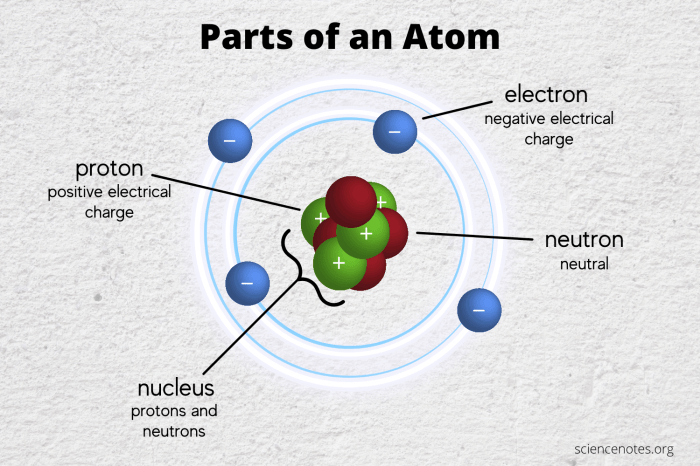
Atoms are the fundamental building blocks of matter. They are incredibly small, with a diameter of about 10^-10 meters. Atoms are composed of even smaller particles called subatomic particles. The three main types of subatomic particles are protons, neutrons, and electrons.
Protons are positively charged particles located in the nucleus of an atom. Neutrons are neutral particles also located in the nucleus. Electrons are negatively charged particles that orbit the nucleus.
The relative sizes of these particles vary greatly. Protons and neutrons are about 10^-15 meters in diameter, while electrons are about 10^-18 meters in diameter.
The charges of these particles also vary. Protons have a positive charge of +1, neutrons have a neutral charge of 0, and electrons have a negative charge of -1.
Structure of an Atom
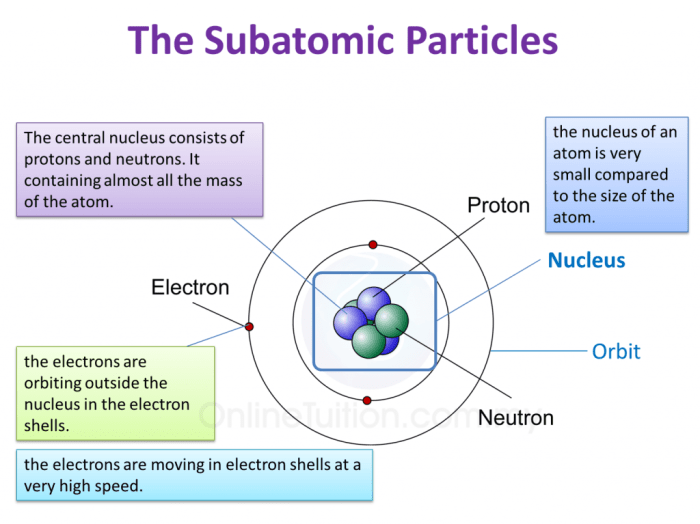
The structure of an atom can be visualized using a concept map:
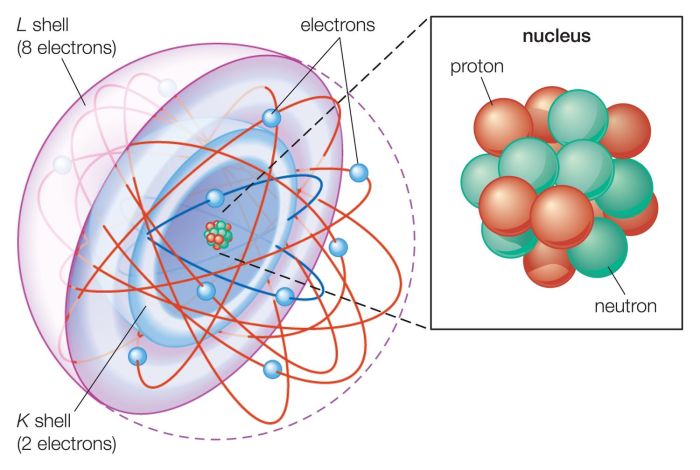
- Nucleus:The nucleus is the central part of an atom and contains the protons and neutrons.
- Electrons:The electrons orbit the nucleus in shells or energy levels.
- Energy levels:The energy levels are arranged in shells around the nucleus. Each shell can hold a specific number of electrons.
The nucleus is very dense and contains most of the mass of the atom. The electrons are much less massive and orbit the nucleus at high speeds.
Properties of Subatomic Particles
Protons:
- Mass:1 atomic mass unit (amu)
- Charge:+1
- Spin:1/2
Neutrons:
- Mass:1 amu
- Charge:0
- Spin:1/2
Electrons:
- Mass:1/1836 amu
- Charge:-1
- Spin:1/2
The mass of an atom is determined by the number of protons and neutrons it contains. The atomic number of an atom is the number of protons it contains.
Interactions Between Subatomic Particles
Electromagnetic force:The electromagnetic force governs interactions between protons and electrons. Protons have a positive charge and electrons have a negative charge, so they attract each other. This force is responsible for holding atoms together.
Strong nuclear force:The strong nuclear force holds protons and neutrons together in the nucleus. This force is much stronger than the electromagnetic force, but it only acts over very short distances.
Weak nuclear force:The weak nuclear force is responsible for radioactive decay. This force is responsible for the decay of neutrons into protons and electrons.
Applications of Understanding Subatomic Particles
The understanding of subatomic particles has led to numerous technological advancements, including:
- Particle accelerators:Particle accelerators are used to study the properties of subatomic particles. These accelerators can reach very high energies, which allows scientists to create new particles and study their interactions.
- Medical applications:Subatomic particles are used in a variety of medical applications, including cancer treatment and medical imaging.
- Nuclear energy:Nuclear energy is a source of energy that is produced by the splitting of atoms. This process releases a great amount of energy, which can be used to generate electricity.
Query Resolution
What are the fundamental building blocks of matter?
Atoms, composed of subatomic particles including protons, neutrons, and electrons.
Where are protons and neutrons located within an atom?
Protons and neutrons reside in the nucleus, the central core of the atom.
What force governs the interactions between protons and electrons?
The electromagnetic force orchestrates the interactions between protons and electrons.