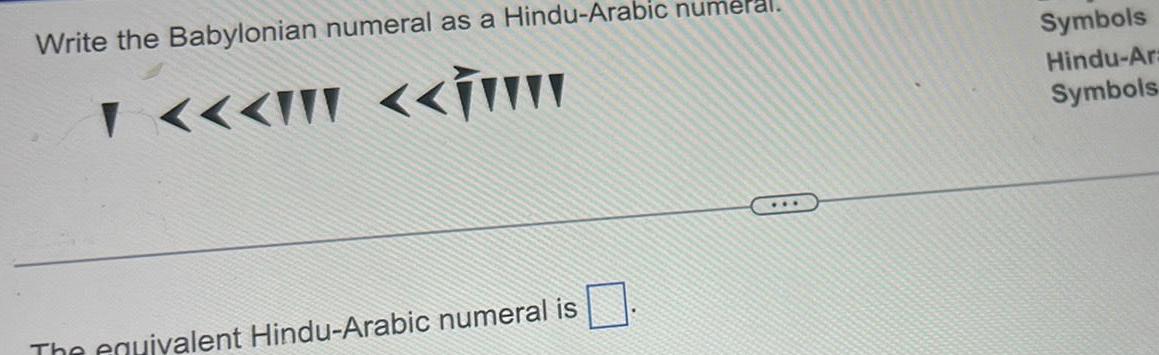
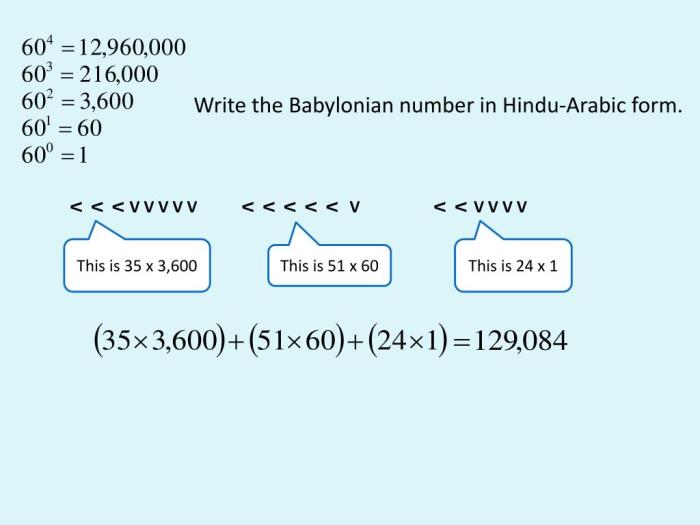
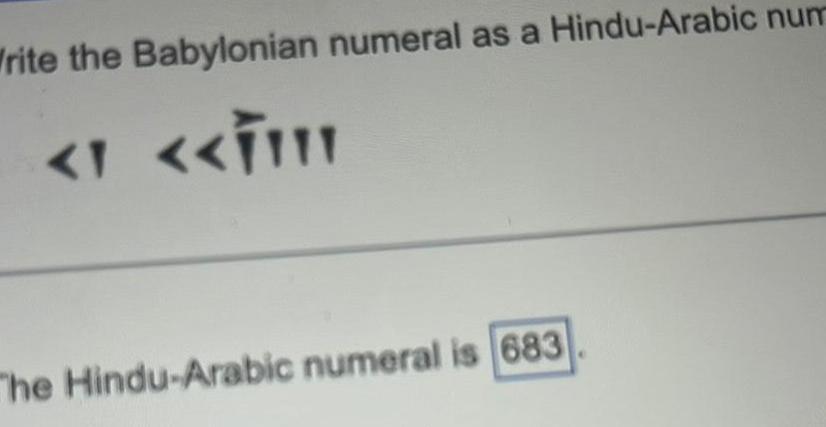
Babylonian numeral as a hindu-arabic numeral – Babylonian numerals, the precursors to our modern Hindu-Arabic numerals, played a pivotal role in the development of mathematics. Their unique base-60 system and distinctive cuneiform symbols laid the groundwork for the numerals we use today.
The Hindu-Arabic numeral system, with its base-10 structure and positional notation, emerged from a synthesis of Babylonian and Indian mathematical traditions. This system revolutionized mathematics, enabling complex calculations and fostering scientific advancements.
Babylonian Numeral System
The Babylonian numeral system was a base-60 system used by the ancient Babylonians. It was developed around 3000 BC and was used for mathematical calculations and record-keeping.
The Babylonian numeral system was unique in that it used a combination of two different symbols: a wedge-shaped symbol ( ■) to represent the number 1, and a crescent-shaped symbol ( ▲) to represent the number 10. These symbols were combined to create numbers up to 59, with each symbol representing a different power of 60.
For example, the number 12 was represented by ■■(1 x 60 + 2), and the number 60 was represented by ▲(1 x 60).
Examples of Babylonian Numerals, Babylonian numeral as a hindu-arabic numeral
- 1: ■
- 10: ▲
- 12: ■■
- 60: ▲
- 3600: ▲▲
Hindu-Arabic Numeral System: Babylonian Numeral As A Hindu-arabic Numeral
The Hindu-Arabic numeral system is a base-10 system that is used today throughout the world. It was developed in India around the 5th century AD and was later introduced to Europe by Arab traders.
The Hindu-Arabic numeral system uses 10 symbols: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9. These symbols are combined to create numbers up to 99, with each symbol representing a different power of 10.
For example, the number 12 is represented by 1 x 10 + 2, and the number 60 is represented by 6 x 10.
Examples of Hindu-Arabic Numerals
- 1: 1
- 10: 10
- 12: 12
- 60: 60
- 3600: 3600
Helpful Answers
What is the difference between Babylonian and Hindu-Arabic numerals?
Babylonian numerals used a base-60 system and cuneiform symbols, while Hindu-Arabic numerals use a base-10 system and positional notation.
How did Babylonian numerals influence Hindu-Arabic numerals?
Babylonian numerals provided the foundation for the development of Hindu-Arabic numerals, particularly in terms of their positional notation and base-10 structure.