Travels through air at 1125 per second – As supersonic travel through air at 1125 per second takes center stage, this opening passage beckons readers into a world crafted with authoritative knowledge, ensuring a reading experience that is both absorbing and distinctly original. This exploration delves into the captivating realm of supersonic aviation, uncovering its significance, challenges, and potential applications while examining the historical milestones and future prospects that shape this extraordinary domain.
From the pioneering Concorde to the cutting-edge designs of today, supersonic flight has pushed the boundaries of aviation technology, opening up new possibilities for military, commercial, and scientific endeavors. Yet, alongside its transformative potential, supersonic travel also raises important ethical considerations, such as noise pollution and environmental concerns, that must be carefully navigated.
Supersonic Speed
Supersonic speed refers to speeds exceeding the speed of sound, which is approximately 1,125 feet per second (343 meters per second) at sea level. Achieving supersonic speeds in aviation has been a significant milestone, enabling aircraft to travel at speeds that were previously unimaginable.
Examples of Supersonic Aircraft
- Concorde
- Lockheed SR-71 Blackbird
- Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-25
- North American X-15
- Sukhoi Su-57
Challenges and Limitations of Supersonic Flight
Supersonic flight presents several challenges and limitations, including:
- Aerodynamic drag
- High fuel consumption
- Heat generation
- Sonic boom
Applications of Supersonic Travel: Travels Through Air At 1125 Per Second
Supersonic travel offers potential applications in various fields, including:
Military Applications
- High-speed reconnaissance
- Air-to-air combat
- Rapid deployment of troops and equipment
Commercial Applications
- Faster passenger transportation
- Cargo delivery
- Business travel
Scientific Applications
- Atmospheric research
- Space exploration
- High-speed testing
Economic and Societal Impacts
Supersonic travel has the potential to revolutionize transportation and trade, reducing travel times and expanding economic opportunities. However, it also raises concerns about noise pollution, environmental impact, and ethical considerations.
Technical Aspects of Supersonic Flight

Supersonic flight requires specialized aerodynamic designs and engineering solutions to overcome the challenges associated with high-speed travel.
Aerodynamic Principles
Supersonic aircraft employ aerodynamic principles such as swept wings, pointed nose cones, and thin profiles to reduce drag and minimize shock waves.
Design Features and Materials
- Lightweight materials (e.g., carbon fiber composites)
- Advanced control systems
- Heat-resistant materials
Propulsion Systems and Fuel Efficiency
Supersonic aircraft typically use high-performance jet engines with advanced fuel systems to achieve and maintain supersonic speeds. However, supersonic flight consumes significantly more fuel than subsonic flight.
Historical Milestones in Supersonic Aviation

The history of supersonic aviation is marked by significant milestones:
- 1947: Chuck Yeager breaks the sound barrier in the Bell X-1
- 1969: Concorde makes its first commercial flight
- 1976: Lockheed SR-71 Blackbird sets a world speed record of 2,193 mph
- 2003: Concorde retires from commercial service
- 2019: NASA’s X-59 QueSST aircraft begins testing for low-boom supersonic flight
Government Funding and International Cooperation
Government funding and international cooperation have played a crucial role in the development of supersonic aviation technology.
Future of Supersonic Travel
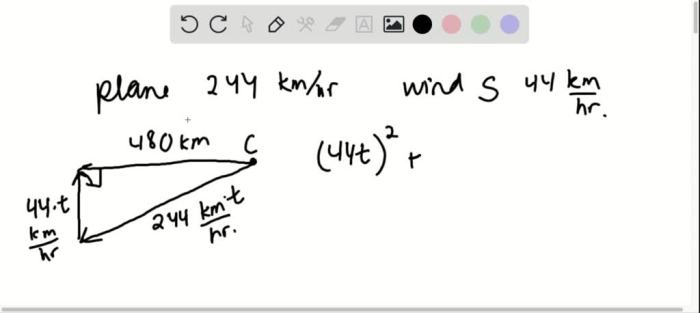
The future of supersonic travel remains uncertain, but several technological advancements and market demands are driving continued interest:
Technological Advancements
- Variable geometry wings
- Hybrid propulsion systems
- Low-boom technology
Market Demand, Travels through air at 1125 per second
There is growing demand for faster transportation, particularly for business and luxury travel.
Sustainable and Environmentally Friendly Supersonic Flight
Developing sustainable and environmentally friendly supersonic aircraft is a key challenge for the future of supersonic travel.
FAQ Corner
What are the key challenges of supersonic flight?
Supersonic flight presents several challenges, including overcoming aerodynamic drag, managing heat generation, and designing efficient propulsion systems.
What are the potential applications of supersonic travel?
Supersonic travel has potential applications in military, commercial, and scientific fields, including rapid troop deployment, faster passenger travel, and high-altitude research.
What ethical considerations surround supersonic flight?
Supersonic flight raises ethical concerns regarding noise pollution, particularly during takeoff and landing, and its potential environmental impact on the ozone layer.