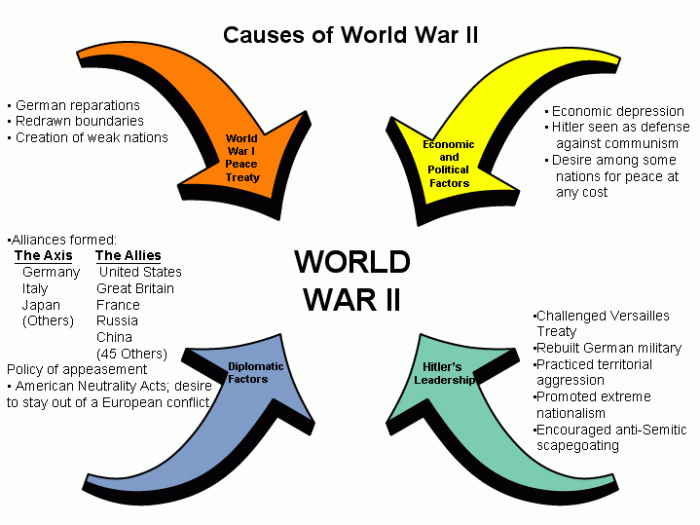
Long term causes of ww2 in europe – The long-term causes of World War II in Europe form a complex and multifaceted tapestry of political, economic, social, military, and diplomatic factors. Understanding these long-term causes is crucial for grasping the origins and consequences of this devastating conflict.
The Treaty of Versailles, economic depression, rise of totalitarian regimes, and diplomatic failures played significant roles in creating the conditions that led to the outbreak of war.
Political and Ideological Factors

After World War I, Europe experienced a surge in nationalism and militarism. Countries sought to assert their power and protect their interests, leading to increased tensions and competition. The Treaty of Versailles, imposed on Germany after the war, was particularly divisive.
It stripped Germany of territories, imposed heavy reparations, and limited its military strength. This humiliation and resentment fueled German nationalism and instability, contributing to the rise of the Nazi Party.
Totalitarian Regimes
The interwar period also witnessed the emergence of totalitarian regimes in Italy, Germany, and the Soviet Union. These regimes, led by charismatic dictators, suppressed political opposition, controlled the media, and pursued aggressive expansionist policies. Their ideologies, including fascism, Nazism, and communism, glorified war and conquest, and promoted the idea of a superior race or nation.
Economic and Social Conditions
Economic Crisis of the 1930s
The Great Depression, a severe economic crisis that began in 1929, had a devastating impact on European economies. Unemployment soared, poverty increased, and social unrest grew. The crisis undermined confidence in democratic governments and created a fertile ground for extremist ideologies that promised economic recovery and stability.
Social Unrest
The economic crisis exacerbated existing social inequalities and tensions. Poverty, unemployment, and a lack of opportunities led to widespread discontent and political radicalization. The rise of mass unemployment and the erosion of the middle class created a sense of insecurity and desperation, making people more susceptible to appeals from extremist groups.
Military and Strategic Developments

New Military Technologies
The interwar period saw significant advances in military technology. The development of new weapons, such as aircraft, tanks, and submarines, revolutionized warfare. The emergence of air power and the concept of Blitzkrieg (lightning war) gave countries with superior air forces and mechanized armies a significant advantage.
Military Alliances
As tensions escalated, European countries sought to strengthen their positions by forming military alliances. France and Poland signed a mutual defense treaty, while Germany and the Soviet Union entered into the Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact. These alliances further divided Europe and increased the likelihood of a wider conflict.
Diplomatic Failures and Miscalculations
League of Nations
The League of Nations, established after World War I to prevent future conflicts, failed to effectively address the growing tensions in Europe. It lacked the power to enforce its resolutions and was unable to resolve disputes peacefully.
Appeasement, Long term causes of ww2 in europe
In the face of German aggression, Britain and France pursued a policy of appeasement, hoping to avoid war by conceding to German demands. However, appeasement only emboldened Germany and increased its territorial ambitions.
Munich Agreement
The Munich Agreement, signed in 1938, was a major diplomatic failure that allowed Germany to annex the Sudetenland, a part of Czechoslovakia. This agreement was widely seen as a betrayal of Czechoslovakia and further weakened the League of Nations.
Key Questions Answered: Long Term Causes Of Ww2 In Europe
What were the key political factors that contributed to the outbreak of World War II in Europe?
The rise of nationalism, militarism, and totalitarian regimes in Europe after World War I created tensions and rivalries that fueled the conflict.
How did the Treaty of Versailles contribute to the long-term causes of World War II?
The Treaty of Versailles imposed harsh reparations and territorial losses on Germany, creating resentment and instability that contributed to the rise of Nazi Germany.
What was the role of economic factors in the lead-up to World War II?
The Great Depression of the 1930s caused widespread unemployment, poverty, and social unrest, creating fertile ground for the rise of extremist ideologies and political instability.