Project 2.3 2 diabetic emergency – Project 2.3.2: Diabetic Emergencies delves into the critical aspects of recognizing and managing diabetic emergencies, equipping individuals with the knowledge and skills to respond effectively to these life-threatening situations.
Understanding the signs, symptoms, and appropriate treatment protocols is paramount in ensuring optimal patient outcomes and preventing complications. This comprehensive project provides a structured framework for managing diabetic emergencies, empowering healthcare professionals and individuals alike to respond confidently and effectively.
Diabetic Emergency: Project 2.3 2
Diabetic emergencies are serious medical conditions that require immediate attention. Recognizing and managing these emergencies is crucial to prevent severe complications or even death. This project aims to provide a comprehensive overview of diabetic emergencies, including their signs, symptoms, treatment, and prevention strategies.
Signs and Symptoms of a Diabetic Emergency: Project 2.3 2 Diabetic Emergency
The signs and symptoms of diabetic emergencies can vary depending on the type of diabetes (Type 1 or Type 2) and the severity of the condition. The following table summarizes the most common signs and symptoms:
| Type 1 Diabetes | Type 2 Diabetes |
|---|---|
| Hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) | Hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) |
| DKA (diabetic ketoacidosis) | HHS (hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state) |
| Hyperosmolar hyperglycemic nonketotic syndrome (HHNK) | Euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis (eDKA) |
Treatment for Diabetic Emergencies
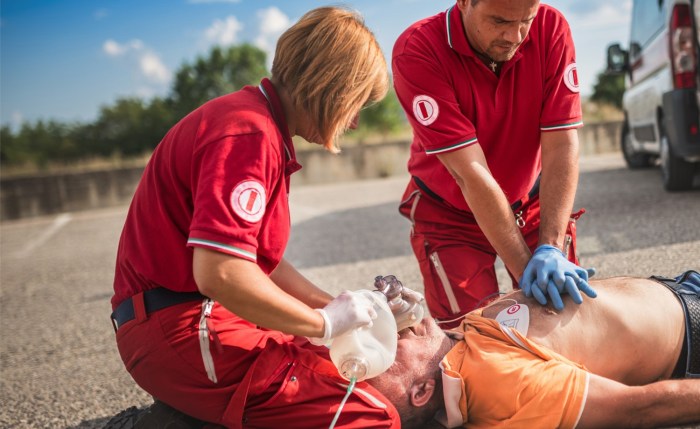
- Call for emergency medical services (911 or your local emergency number) immediately.
- Administer glucagon (for hypoglycemia) or insulin (for hyperglycemia) as directed by a healthcare professional.
- Monitor blood glucose levels and adjust treatment accordingly.
- Provide fluids and electrolytes as needed.
- Transport the patient to the nearest hospital for further treatment and monitoring.
Prevention of Diabetic Emergencies
Preventing diabetic emergencies is crucial for individuals with diabetes. The following tips can help reduce the risk of these emergencies:
- Monitor blood glucose levels regularly and follow the treatment plan prescribed by a healthcare professional.
- Recognize the signs and symptoms of diabetic emergencies and seek medical attention promptly.
- Make healthy lifestyle choices, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management.
- Attend regular medical check-ups to assess diabetes management and prevent complications.
Question Bank
What are the most common signs of a diabetic emergency?
Common signs include confusion, disorientation, excessive thirst, frequent urination, rapid breathing, fruity breath odor, and abdominal pain.
What should I do if I suspect someone is experiencing a diabetic emergency?
Call for emergency medical services immediately and provide the individual with sugary drinks or food if they are conscious.
How can I prevent diabetic emergencies?
Regular blood glucose monitoring, adhering to medication regimens, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle can help prevent emergencies.